How A Car Battery Works?
Battery
Working Of Car Battery
A car battery is the base for electrical power that a car uses while in operation and while the ignition key is in the "ON" position without the engine running. This battery stores electric energy to start the engine and operate electrical accessories in the electrical system throughout the car when the engine is not running. Car batteries are equipped with a positive and negative terminals from which the battery cables are attached. Battery cables route power from the battery to the power distribution center and engine block. Because most batteries are filled with acid, use caution when working or testing a battery by wearing protective eyewear, gloves and clothing.
A battery work in two ways, first it supplies the voltage the car needs to operate, next it produces enough amperage to turn the starter motor. If the battery fails in either of these categories the engine will not start, or the cars engine will stall. Most repair shops have a amperage tester but you can perform your own amperage draw test using the vehicle as the tester. Visit - Battery testing
A car battery is a rechargeable cell in the SLI (starting-lighting-ignition) variety of batteries which are lead acid based. Lead acid batteries are the oldest style of rechargeable batteries. The high power electrical output of a car battery is necessary to supply a current needed for the engine starter. A normal car battery provides about 12.6 volts and is divided into 6 separate cells, each cell produces about 2.1 volts per cell. As the battery state of charge decreases the voltage produced also decreases. Battery power is created through a chemical reaction where positive and negative lead plates are immersed in an electrolyte solution (battery acid).
This solution is a combination of water and sulfuric acid. When the solution interacts with the lead plates, the chemical interaction creates voltage. This voltage is then released through the batteries positive terminal (red) and returned to the negative terminal (black). Voltage from the alternator maintains the batteries state of charge. This continuous cycle can produce electricity for years.
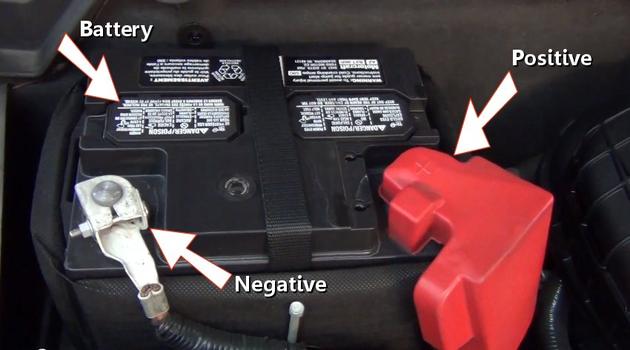
Car Battery
Common Problems
The most common way to recharge your battery is by a process called trickle charging. This is performed using an inexpensive trickle charger. Most repair shops have a more powerful and more expensive battery charger that is capable of charging at a higher rate over a shorter time period. To jump start a car, a set of jumper cables is needed. Visit - Jump start battery
When replacing a battery its important to match the terminals (negative and positive) to the new replacement battery. Visit - Battery replacement
Once the battery replacement is complete, start the engine and check the charging system. Visit - Alternator test
Battery Caution
When the battery is overcharged or jump started, water in the electrolyte solution is transformed into hydrogen and oxygen. This can cause an explosion from the battery if a spark or another source of ignition is present. It also decreases the fluid level inside the battery and can expose the lead plates. Exposure to oxygen can damage these plates and reduces their ability to provide the chemical reaction needed. Inspect your battery regularly, if acid is present replace the battery and check the charging system. Be extremely careful when handling a car battery, gloves and eye protection are recommended as battery acid is highly corrosive. When charging a battery use caution, always connect the charge leads while the charger is OFF, this will prevent a spark from being created. A battery is prone to an explosion after a battery charge.
Clean Battery and Terminals
There are deposits that can form on the battery terminals. These deposits are corrosive by-products of a normal battery charge and discharge function. While wearing protective goggles and clothing, use a garden hose to rinse the battery completely also rinse the surrounding area, this will dilute the acid to a non-corrosive state. You can also apply baking soda to help neutralize the battery acid. Use a wire brush on the battery terminals to clean thoroughly and reassemble, recheck charging system as needed.
Battery Storage
If excessive corrosion on battery cables are observed they should be replaced. Corrosion can cause high resistance resulting in a starter operation failure. Avoid using after market cables as they may not be manufactured to proper specifications resulting in poor battery performance. Visit - Battery cable replacement
Recycling Old Batteries
An old car battery is completely recyclable, contact your local recycling station, auto part store or repair garage. Do not discard old batteries in land fills.

Car Battery
The most common way to recharge your battery is by a process called trickle charging. This is performed using an inexpensive trickle charger. Most repair shops have a more powerful and more expensive battery charger that is capable of charging at a higher rate over a shorter time period. To jump start a car, a set of jumper cables is needed. Visit - Jump start battery
- Fully charge battery
- Store in a cool place but not where it will be below 0 C or 32 degrees Fahrenheit
- Check the battery every two months and recharge if needed
- Remove all electrical connectors from the battery
Comments
Post a Comment