Car Engine Overheat
Troubleshooting Car Engine Overheating Issues
Helpful Information
Make sure to service your engine coolant per your manufacturers recommendation.
Step by step guide on how to troubleshoot and repair an automotive engine overheating or running hot problems, this information pertains to most cars.
Difficulty Scale: 4 of 10
Begin with the vehicle on level ground, engine cold (off) in park with the emergency brake set.
Step 1 - Engine coolant is used to transfer heat from the engine to the radiator, over time this coolant can dissipate and lose effectiveness. To check this fluid wait until the engine is cold, slowly remove the radiator cap, a small amount of pressure maybe released which is normal, add coolant to just above the minimum level marker. Low levels of coolant can lead to problems related to engine overheating. Always maintain proper levels of coolant in the overflow coolant reservoir tank also, re install the cap properly.
 Adding Engine Coolant (Red)
Adding Engine Coolant (Red)
Step 2 - If a low coolant level is persistent or a noticeable leak is detected the engine will overheat or run hot. If engine overheating has occurred the coolant level will naturally be low due to expansion of the coolant from the extreme heat of the engine. This heat expansion forces coolant out of the radiator and coolant reservoir. To test for a coolant leak move the car to a dry smooth surface and allow the engine to cool. Remove the radiator cap and carefully (do not spill) add water until full, then re-install cap. Start engine and allow to run for about three to five minutes (do not allow to overheat) while the engine is running inspect the ground below the engine, if an engine coolant leak is present observe the location of the coolant drops, this will help determine where to start looking for the coolant leak (shut the engine off before inspecting).
 Green Coolant Leak
Green Coolant Leak
 Step 3 - A radiator cooling fan is used to move air through the radiator cooling fins which helps cool the engine. If this fan stops operating the engine will overheat or run hot. To inspect an electric motor cooling fan, start with ignition key switch "OFF", next spin the fan blade by hand, it should "freewheel" if the fan motor does not spin freely it has failed and needs to be replaced. To check this fan operation allow the engine to cool, start the engine and turn the
Step 3 - A radiator cooling fan is used to move air through the radiator cooling fins which helps cool the engine. If this fan stops operating the engine will overheat or run hot. To inspect an electric motor cooling fan, start with ignition key switch "OFF", next spin the fan blade by hand, it should "freewheel" if the fan motor does not spin freely it has failed and needs to be replaced. To check this fan operation allow the engine to cool, start the engine and turn the air conditioner
to the coolest setting. Within two minutes of the car air conditioner operating the cooling fans
should activate, if not, the fan motor fuse must be checked first; if the fuse condition is okay, the remainder of the electrical system must be checked. To further troubleshoot this problem a wiring schematic is needed. A cooling fan motor failure is very a common failure
Radiator Cooling Fan
Step 4 - A cooling system thermostat is used to restrict coolant flow when the engine is cold which helps the engine to heat up to and then maintain operating temperature. If the thermostat sticks closed the engine will overheat within a short amount of time.
 Engine Cooling System Thermostat
Engine Cooling System Thermostat
Step 5 - A water or coolant pump is used to circulate fluid in and around the block which aids the cooling system's operation. If this pump fails either internally or by leaking coolant, it must be replaced.
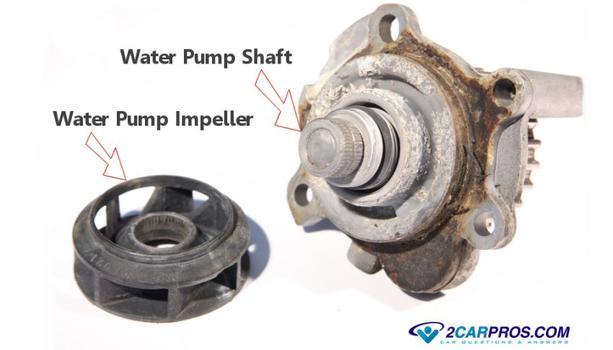 Water Pump Failure
Water Pump Failure
Step 6 - When a cooling system is neglected it can cause the radiator to become plugged causing the engine to overheat or run hot. When the engine is cold remove the radiator cap and inspect the internal cooling tubes for corrosion.
 Plugged Radiator
Plugged Radiator
Inside the radiator many small tubes which are constructed with cooling fins transfer heat to the atmosphere. If the radiator becomes plugged it fails to transfer heat from the coolant causing the engine to overheat. This condition generally occurs gradually over time and will be more noticeable when climbing a grade or in warm weather. To check for this condition make sure the engine is cold, and then drain coolant to lower the level in the radiator, this will allow visual inspection of the cooler tubes in the radiator core. If the radiator cooler tubes are plugged drain the cooling system completely and replace the radiator with new, reassemble and refill with coolant and recheck system.
 Plugged Radiator
Plugged Radiator
Step 7 - Air flow is needed to dissipate heat from the radiator. Even if the inside of the radiator is clear, the outside air flow can be blocked by dirt and debris causing the engine to overheat. Use a garden hose to pressure wash the radiator from the backside facing forward. (backflush)
 Blocked Radiator
Blocked Radiator
Step 8 - On some cars a thematic fan clutch is attached to the engine which controls the fan operation according to temperature of the radiator. When this component goes bad it fails to "lock up" which diminishes it's performance causing the engine to overheat.
 Thermo Fan Clutch
Thermo Fan Clutch
Step 9 - A head gasket is used to seal the combustion process within the engine block and cylinder head(s). When this gasket fails it can cause overheating and occasionally rough running.
 Blown Head Gasket
Blown Head Gasket
Step 10 - When a catalytic converter fails
it will partially plug the exhaust system creating excessive backpressure in the exhaust system which causes the engine to have less power. To compensate for this low power condition the driver will increase the throttle which then creates excessive heat overloading the cooling system causing overheating. This condition is always accompanied by low engine power.
 Plugged Catalytic Converter
Plugged Catalytic Converter


 Step 3 - A radiator cooling fan is used to move air through the radiator cooling fins which helps cool the engine. If this fan stops operating the engine will overheat or run hot. To inspect an electric motor cooling fan, start with ignition key switch "OFF", next spin the fan blade by hand, it should "freewheel" if the fan motor does not spin freely it has failed and needs to be replaced. To check this fan operation allow the engine to cool, start the engine and turn the air conditioner to the coolest setting. Within two minutes of the car air conditioner operating the cooling fans should activate, if not, the fan motor fuse must be checked first; if the fuse condition is okay, the remainder of the electrical system must be checked. To further troubleshoot this problem a wiring schematic is needed. A cooling fan motor failure is very a common failure
Step 3 - A radiator cooling fan is used to move air through the radiator cooling fins which helps cool the engine. If this fan stops operating the engine will overheat or run hot. To inspect an electric motor cooling fan, start with ignition key switch "OFF", next spin the fan blade by hand, it should "freewheel" if the fan motor does not spin freely it has failed and needs to be replaced. To check this fan operation allow the engine to cool, start the engine and turn the air conditioner to the coolest setting. Within two minutes of the car air conditioner operating the cooling fans should activate, if not, the fan motor fuse must be checked first; if the fuse condition is okay, the remainder of the electrical system must be checked. To further troubleshoot this problem a wiring schematic is needed. A cooling fan motor failure is very a common failure 







Great explanation
ReplyDelete