How A Car Electrical System Works? PART 2
Vehicles Electrical System
CHECK PART 1 FOR PREVIOUS DETAILSStep 19 - The ignition switch is what controls the electrical system within a locking mechanism that utilizes a key for safety. This key possess a frequency chip as an added theft deterrent.

Ignition Switch

Information Control Center

Climate Control Center
 Step 22 - The instrument cluster is used to monitor engine and others system via gauges and warning lights.
Step 22 - The instrument cluster is used to monitor engine and others system via gauges and warning lights.
Door Lock Switch

Interior Lighting
Step 25 - The lighting system is used to illuminate the vehicle for safety and convenience. The rear lights include, tail, brake, reverse and license plate bulbs.

Rear Lights

Front Lights
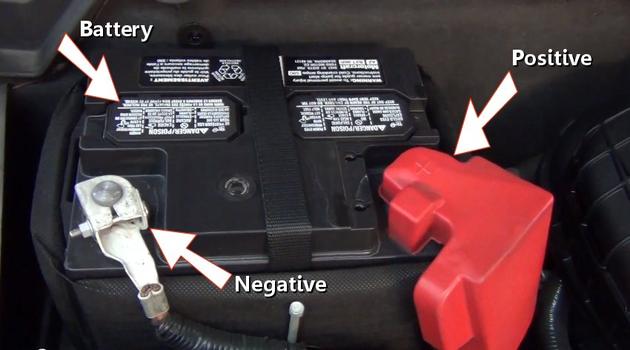
Automotive Battery
 Step 28 - The negative side of thebattery is connected to the body, and engine block of the vehicle which acts as a connector for the positive battery power completing the electrical circuit.
Step 28 - The negative side of thebattery is connected to the body, and engine block of the vehicle which acts as a connector for the positive battery power completing the electrical circuit.
Comments
Post a Comment